2024 Year in Review: Dual Enrollment Legislation
Tracking State Progress Toward Equitable College in High School Opportunities
In 2024, state policymakers across the country continued to strengthen access to college in high school programs such as dual enrollment, concurrent enrollment, and early college high school. While the overall number of new laws decreased from the record pace of 2023, states remained active in refining systems that support equitable student access, quality, and sustainability.
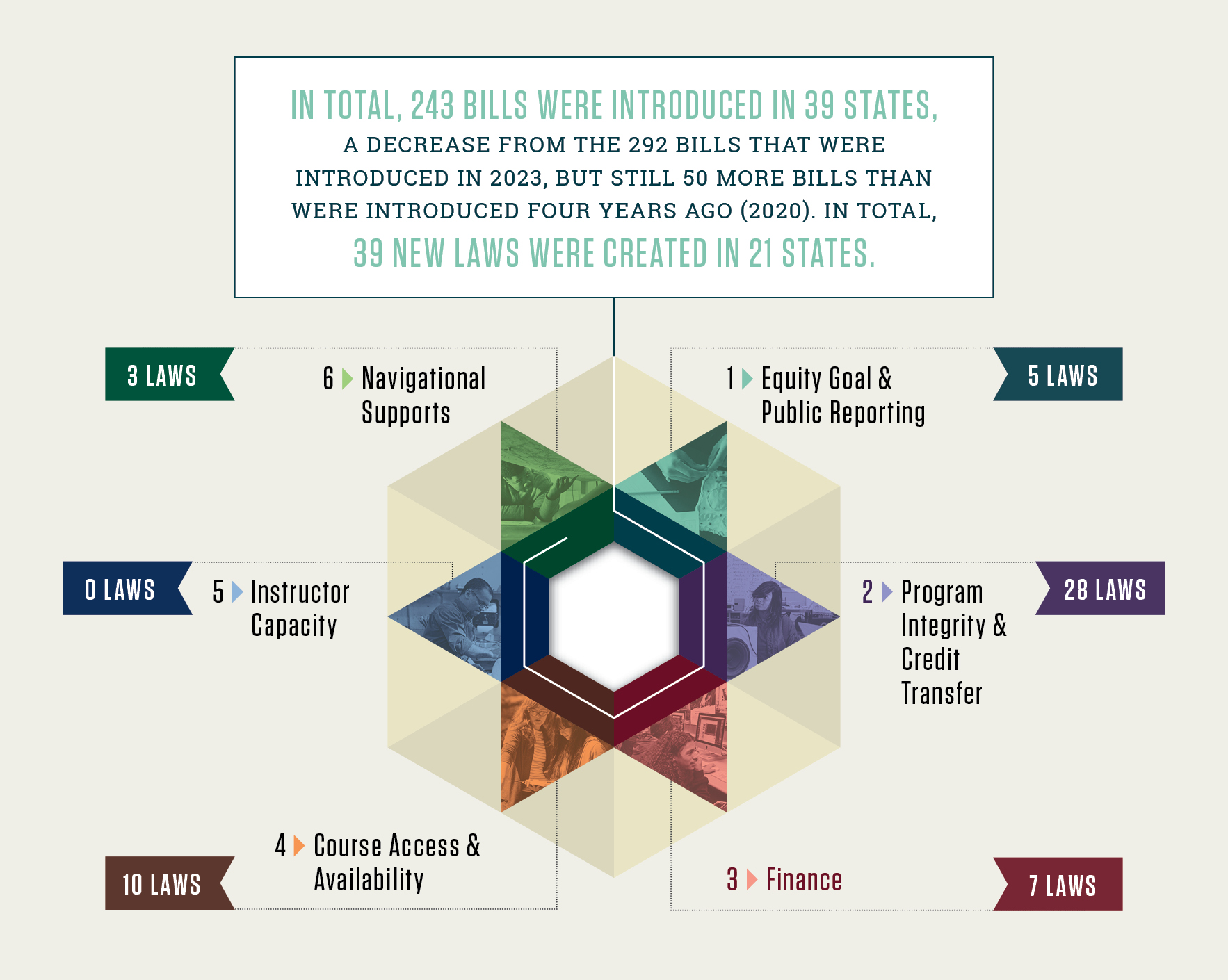
According to CHSA’s 2024 Year in Review State Legislative Tracker, 243 bills were introduced across 39 states, resulting in 39 new laws enacted in 21 states. Though down slightly from 2023’s totals, this represents more than 50 additional bills compared to just four years ago — signaling strong and sustained legislative attention to college in high school programs nationwide
Top Areas of Legislative Activity
Using CHSA’s Unlocking Potential: A State Policy Roadmap for Equity and Quality in College in High School Programs as a framework, the 2024 legislative activity was most concentrated in:
-
Course Access & Availability (10 laws enacted)
-
Program Integrity & Credit Transfer (7 laws enacted)
-
Finance (5 laws enacted)
-
Equity Goals & Public Reporting (3 laws enacted)
-
Navigational Supports (3 laws enacted)
-
Instructor Capacity (0 laws enacted)
These categories highlight where states are most focused — expanding who can access programs, ensuring credit transfer, and building financial models that sustain growth.
Notable 2024 Laws
Several states passed standout legislation with the potential to significantly expand access and improve student outcomes:
-
California (SB 153) – Requires use of eTranscript California to simplify how dual enrollment courses and grades appear on high school transcripts, improving transferability and transparency.
-
Connecticut (SB 14) – Authorizes a statewide study on creating a coordinated dual enrollment system to better serve students across the state.
-
Idaho (SB 1359) – Increases student funding in the Advanced Opportunities program from $4,125 to $4,625, expanding support for dual credit and other early college options.
-
Tennessee (HB 1923) – Requires Tennessee Colleges of Applied Technology to reserve post-graduation enrollment slots for their dual enrollment students, promoting seamless transitions to college.
-
Virginia (SB 627) – Establishes the College and Career Ready Virginia Fund to expand statewide access to tuition-free dual enrollment courses.
-
Washington (HB 1146) – Requires high schools to inform students and parents about all available dual credit programs and financial aid options
Key Trends to Watch
After several years of rapid policy growth, 2024 marked the first slight slowdown in dual enrollment legislation since 2020. This shift reflects two main realities:
-
Implementation Mode: Many states are now focused on implementing and assessing recently enacted dual enrollment reforms.
-
Budget Pressures: With pandemic-era federal funds expiring, states are balancing tight budgets while trying to sustain expanded educational opportunities.
Even so, legislative activity remains high, and states continue to innovate to promote equitable access, affordability, and quality in college in high school programs.
Explore the Full Tracker
For detailed summaries of every 2024 dual enrollment bill — including enacted laws, pending legislation, and emerging policy trends — visit the State Legislative and Regulatory Tracker. The tracker will continue to be updated throughout 2025 to reflect new legislative and regulatory developments nationwide.